The 7 Steps SEO Audit
Last updated on January 2, 2023 at 14:25 PM.The goal of a SEO audit is to gain an understanding of how a website works from the perspective of the search engine, in most cases Google. If you help Google to read and understand your website, the search engine will reward you with more visibility through better rating and positioning in the search engine results pages. In addition, optimizing the usability and content relevance of your offer to your users is an important part of the analysis. This should guide your users easily and without distraction through their individual customer journey, so that they become happy regular customers or regular users as quickly as possible.

What is a SEO Audit?
A SEO audit is a complex analysis procedure that determines the current level of search engine optimization of the website. It shows the status quo of your website as well as its potential for improvement. SEO audits must be carried out regularly. The reasons for this are simple:
- You are in continuous competition with your competitors for the highest position on the search engine results page.
- Search engines revise their algorithm for identifying relevant pages at very short intervals, so checks should be done after each update.
A regular SEO audit starts with daily monitoring of the rankings of your pages for the search terms you focus on. However, tools can also tell you whether any anomalies in performance have been observed that indicate a change in the search engine's ranking algorithm.
So it is always the right time to start with an SEO audit.
5 reasons why SEO pays off economically
While there are many reasons why you should perform a SEO audit, the following 5 show that an SEO audit is also financially worthwhile.
Reason 1: Everyone uses search engines
Every internet user who wants to satisfy a need for information in any way uses a search engine. Since Google has a market coverage of more than 90% worldwide, it is self-evident that every company, every publisher and every private blogger has access to their target group through Google. The more specific the need for information is, the more likely it is that communication will take place in closed groups. However, as Google is still the first choice for most searches, this is where the most economic potential lies.
Reason 2: Win customers without media
Because you as a publisher contribute to Google's success with your valuable information, Google rewards you with visibility to your target audience. As this is free of charge, your only investment is the production costs for the content and its search engine optimized preparation. To my knowledge there is no other platform on which advertising space is made available free of charge.
Reason 3: SEO is sustainable
Once published, every piece of content gets continuously indexed and displayed by Google without any follow-up costs. This is in stark contrast to search engine advertising, where investment is required simply to give customers access to your offer. Unlike SEO, if you pause your online advertising campaign you are automatically invisible.
Reason 4: Equal opportunities for everyone
To Google, is relatively unimportant who you are, where you come from and how big your company is. What matters is whether you can meet the current information needs of the searcher. If so, Google will recommend you as an optimal source. If you also support Google technically with indexing, Google will thank you with higher positioning in the search engine result pages. This allows companies that are relatively unknown, but understand SEO, to rank first on relevant topics, while companies that are known but not digitally transformed are often virtually invisible. Equal opportunities for all means true democracy online.
Reason 5: We can use the findings elsewhere
Google provides you with a lot of data on user behavior in the search engine. This data is made available via an interface. For you, the data becomes visible through tools that tap this API and make the data analyzable in your dashboards. From user behavior you can derive insights and measures that go far beyond SEO, e.g. into which product could be developed for the next season.
SEO is worth it, but...
SEO is worthwhile. But since search engine optimization is a significant cost the investment must be balanced by a commercial return.
Products, such as a Nintendo Switch are more likely to be searched for via a product search engine like Amazon. Here the need for information is small, customers mostly use price and availability to decide their purchase.
If our product is so niche that we can address our target group directly (e.g. via account-based marketing), investment in search engine optimization should be questioned at least in its scope.
SEO is a means to an end.
How does a search engine work?
A search engine is a cataloging program. It relates the elements in its database to the user's search queries. Through the top-list functionality (the most relevant results are at the top) it makes a recommendation.
We think of search engines as Google, however the search function on any website is also a search engine. They might simply have a smaller database and less intelligent algorithms.
The stored elements in the database are the different folders and contents of a website. The indexing is done by a crawler. The evaluation behavior of the crawler is constantly revised and, apart from a few official update announcements, kept secret.
The derivations that you receive from an SEO audit are therefore only created via reverse engineering. They are therefore only conditionally resilient. This means that every SEO recommendation must be given with care.
Which SEO data can we evaluate?
Most SEO tools provide information about keywords, links and the technical infrastructure of a website. By analyzing the connections between these three factors, they draw conclusions about your content, the structure of your website, the search behavior of users and the ratings of your content by third parties.
In addition to this objective data, the tools often provide subjective recommendations for action, as well as individual and less transparently aggregated metrics. In this way, they attempt to replicate the artificial intelligence of Google’s algorithms. Of course, this works to a limited extent, since their technical capacities are exceptionally small compared to Google.
Which SEO tools should you use?
Semrush
Semrush is a SEO tool that provides you with lots of data about keywords, rankings, backlinks and search engine advertising campaigns - on a global scale. Who ranks with which keyword in which position, who is advertising to these searchers, and how does it all look in a monthly comparison? Semrush has the answer to these questions
What makes the tool so special for me is how the raw data is evaluated. For example, gap analyses show you which backlinks, organic keywords and paid keywords your competitors or best practice cases have.
The Keyword Magic Tool is also worth mentioning: Here, Semrush provides a huge list of semantically-related keywords, which can help you to discover content ideas you hadn’t thought of.
The Content Magic Tool is similarly liberating: Here, keywords, Google's autosuggest function and ranking pages are evaluated on a content level. This is a great way to fill up your editorial calendar with ideas.
Ahrefs
Another great SEO all-in-one tool: Keywords, rankings, backlinks and website traffic estimates, all that and more is provided by Ahrefs. Again and again, Ahrefs and Semrush compete against each other in tests. The number of found backlinks often differs, while traffic estimation are usually more similar. Sometimes Semrush will show higher numbers, sometimes Ahrefs.
The Ahrefs Content Explorer is a real USP: Ahrefs gives you the answer to the question of which posts in the net are particularly "resonating". The tool has a gigantic website crawler that reads billions of URLs at regular intervals.
In contrast to Semrush, Ahrefs not only relates keywords and URLs, but also collects titles, meta descriptions, full texts and links. As a result we can find out which reviews for the iPhone SE 2020 (search phrase "iPhone SE 2020" AND "test" with a Title Search) were shared particularly frequently amongst users in a defined period of time. We can also learn which publishers have a particularly high authority and achieved a particularly high number of hits with their reviews.
The ability to analyse content in bulk as well as easily compare backlink profiles makes Ahrefs a very effective tool for link building.
Ubersuggest
Ubersuggest is a free and limited SEO tool in its basic version that offers similar features, but not on such a large scale.
It is not a professional tool, but it is an excellent way to get started in search engine optimization, as the limited functionality means less distraction. Because it is free of charge, I will use this tool in this article.
Honorable Mention: Screaming Frog
One tool should not be missing from this list: Screaming Frog SEO Spider. In contrast to the above mentioned cloud tools, Screaming Frog is installed locally on your computer. It is particularly suitable for the technical analysis of a website.
Soft recommendations are not used here. Instead, you’ll receive reliable data on unreachable pages, redirects, folder structures and metadata, which we can evaluate in many ways.
Screaming Frog does not have its own database of search terms, search queries or external link references. However, you can connect to Google Search Console or the above mentioned Ahrefs for more functionality.
The SEO Audit for SEO beginners in 7 steps
Step 1: Planning the project
Before you start your SEO audit, you should plan how much time and money will be invested in the project. Stick to the 80/20 rule: Since the last 20 percent of optimization devours 80 percent of the budget, weigh up whether these optimizations are necessary.
The first SEO audit for a domain will be your benchmark. At regular intervals, you use monitoring to check whether your theses are correct and whether the measures taken as a result were successful.
Step 2: Read the page
In our example we analyze the domain warbyparker.com and use the tool Ubersuggest. It is perfectly suited for our example, as it can be used free of charge and can be accessed via our browser without registration. Here you can find the scanned domain in our SEO tool. The following picture presents itself to us:
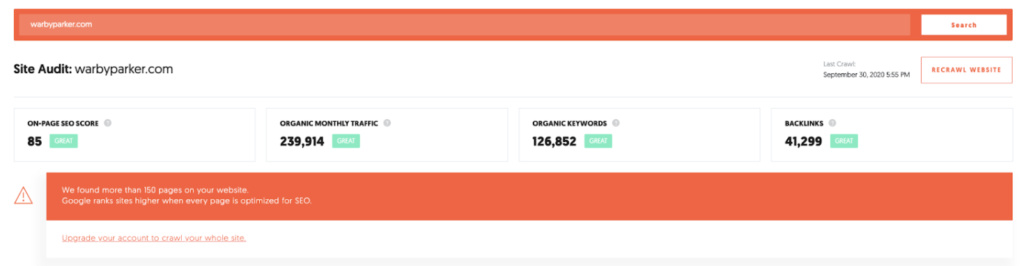
In the middle of your screen you can see a warning message. It says that not all URLs of this domain have been scanned because we work in the free version of the tool. In daily practice this would be a problem, to illustrate our approach this is unproblematic. But please keep in mind that we only analyze 150 URLs here and audit ALL URLs in your project
Otherwise you will find a lot of information about the state of your page on this dashboard. In the next sections we will discuss the different data and interpret them together.
Let's start with the analysis of the technical infrastructure, because these results are the most objective.
Step 3: Check loading time
Google wants to give its users the best possible user experience. And who wants to wait? In the middle of our dashboard we see information about the loading time.
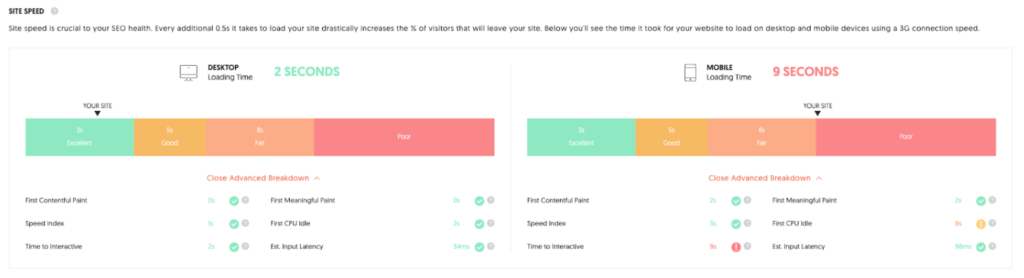
On the left side you see the loading time for the desktop version of the page, on the right side the loading time for the mobile version of the website. You see two different values here. First of all, it is good that there are two versions of this website and one of them is the mobile version. But the mobile version, which is more important to Google, is loading rather slowly.
More than 60% of Google’s search queries come from mobile devices. Therefore Google prefers to index the mobile version of your website first. Users who are on the road often do not have the necessary broadband connection in rural areas, so the mobile version of a website is often a slimmed-down version of the desktop version. This way it loads faster.
In this example, however, we encounter the first problem: The mobile version of the website takes almost five times as long to load as the desktop version.
Below the bars you will find details, e.g. how long it takes to load the first image (2 seconds), when the page becomes interactive (9 seconds) and much more. You can find out what is behind the cryptic names by clicking on the small question marks.
Why does this page load so slowly now? In this case it could be because of uncompressed pictures and videos, code or slow servers. In any case, this is a job for specialists, content managers and developers.
Next we turn to the page and folder structure.
Step 4: Audit the page and folder structure
No user wants to be misled or sent into the void, likewise no one wants to read fragmented or duplicate content, and Google doesn’t want their crawlers to search a server in vain.
Therefore it’s important to check the folder structure of the website as well as the page structure of the individual pages. In the middle of the dashboard you will find the corresponding area:
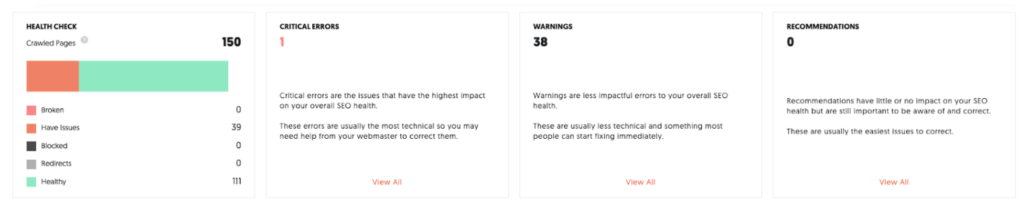
We are interested in the left box. Of the 150 pages examined, 39 have problems and 111 are error-free. This is a mediocre value. You can find out what's behind it by clicking on the box.
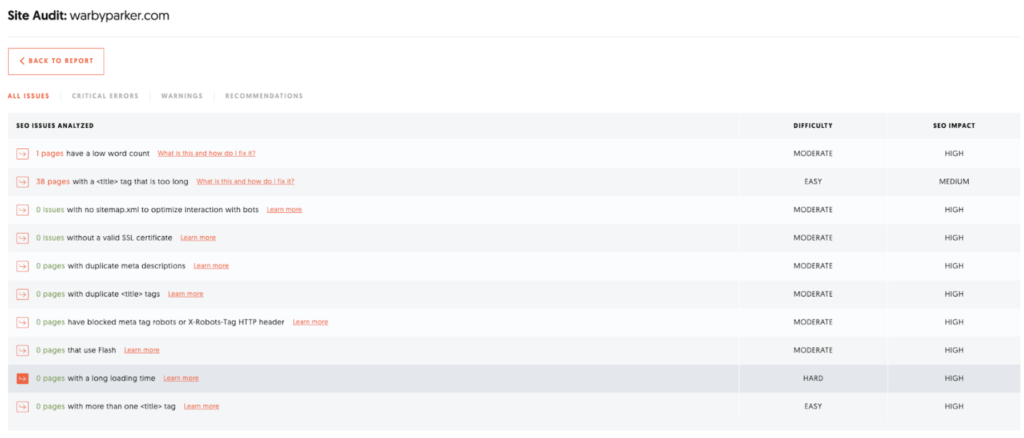
Here you can see a table with all the bugs our tool has identified, as well as its estimation of how complicated it is to fix and how big the impact on SEO performance is. Here it is recommended to consult a SEO specialist who will help to interpret the error messages.
If you follow the recommendations of the tool in our example, you can obviously achieve great success with just a few steps: Increase the word count of one page (to find out which one simply click on the link) and decrease the character count of the title tags of 38 pages.
In this example we do not find any links that point to nowhere (404), no internal link references (301) and no blocked pages. But with 150 examined pages this is not unusual.
All of these errors can be corrected by content managers and editors.
Step 5: Audit keyword rankings
Starting from our Site Audit Dashboard, simply switch over to the Content section and examine the keywords. The third box from the left in the upper part of our Site Audit Dashboard will take us there.

In the following dashboard you can see an overview of the keywords for which we are visible to the search engine user with the individual pages of our domain.

The view is divided into two parts: on the left side you will find the search terms used by users and in the columns of the table you will find information on:
- the number of searches per month,
- your position in the search engine result pages,
- the traffic we would receive from this average ranking (Pay attention here, this is only an estimate), and
- the competition of our competitors for the respective search term.
On the right side we see the list of websites that position themselves on Google's search engine result pages for the search term selected on the left. First, turn to the keywords.
What makes good keywords stand out? Good keywords are keywords,
- which are frequently searched for,
- with which you are already a little visible,
- with which you can attract users to your offer,
- for which there is little competition, and
- that you can capitalize on.
Now let's check the keywords using two examples. At the top of the list you will find the search term "Warby Parker".
Search Keyword "Warby Parker”
The term "Warby Parker" is frequently searched for (volume 823,000). Warby Parker is in the top position, this search term attracts more than 250,000 clicks per month and the level of competition is medium.
Overall, these are promising results, but can the search term "Warby Parker" be capitalized upon?
If you are looking for "Warby Parker", you know Warby Parker. The overall good visibility values are the result of one decade of marketing efforts. These hits do not generate new customers who might otherwise have gone to competitor glassesusa.com. It can be assumed that the aim of the search is the address of the nearest branch. Is it worth the investment to reproduce the Yellow Pages digitally? Not from my point of view, because Google Maps does that all by itself.
Search Keyword "sunglasses”
The search term "sunglasses", on the other hand, corresponds to a search that can be capitalized upon and is relevant to Warby Parker and its market companions.

Again we have a high search volume and many expected clicks, but this business has an invisible ranking outside the top 20.

This is where the content, structural and technical optimization of the affected pages and page areas helps with:
- more thematically complementary content,
- reduction of superfluous content,
- better content structures (internal link references, restructuring of continuous text, use of semantic keywords, W-questions),
- online PR measure for link references from external sources (e.g. guest contributions),
- optimization of loading times
and much more.
This chapter consumes the largest budget of search engine optimization, since it is practically never completed. In any case, these are jobs for content marketers and editors.
Step 6: Audit Backlinks
To do this, go back to your dashboard. In the two middle boxes you will find statements about link references from external domains to our target domain. One click brings us to the backlinks area.

The number of backlinks contains the actual link references found in the database of our tool. "Referring Domains" counts the domains from which these links originate. The larger the number of referring domains, the better. The greater the ratio between backlinks and referring domains, the better also. The maximum is one backlink per domain.
Additionally, the tool shows NoFollow in the area of backlinks, i.e. those backlinks that the search engine crawler should ignore during indexing, and in the area of referring domains, so-called .gov and .edu domains, which the tool considers to be particularly valuable.
The tool shows that this site has an average of 5 backlinks for each domain that is linking to it. If most of these backlinks had identical, keyword-heavy anchor text (the text of the link itself) or there were some unnatural similarities between the linking websites, this could be a negative ranking signal. There are also many plausible reasons why a backlink profile might appear unusual, yet be of no risk to the site owner.
For example, Warby Parker might be running an affiliate program which has resulted in a large number of similar links appearing at the same time. Judging the true quality of a backlink profile means taking a closer look at the link providers and the likely reason the links were created.
Below is a graph showing the growth of backlinks and referring domains over time. It is interesting to note that the number of referrer domains has not grown much, however the number of backlinks has. This looks like a concerted action. Again, you need to take a closer look at what kind of backlinks have been added to the affected domains.
At the bottom we see the backlink generators in table format.
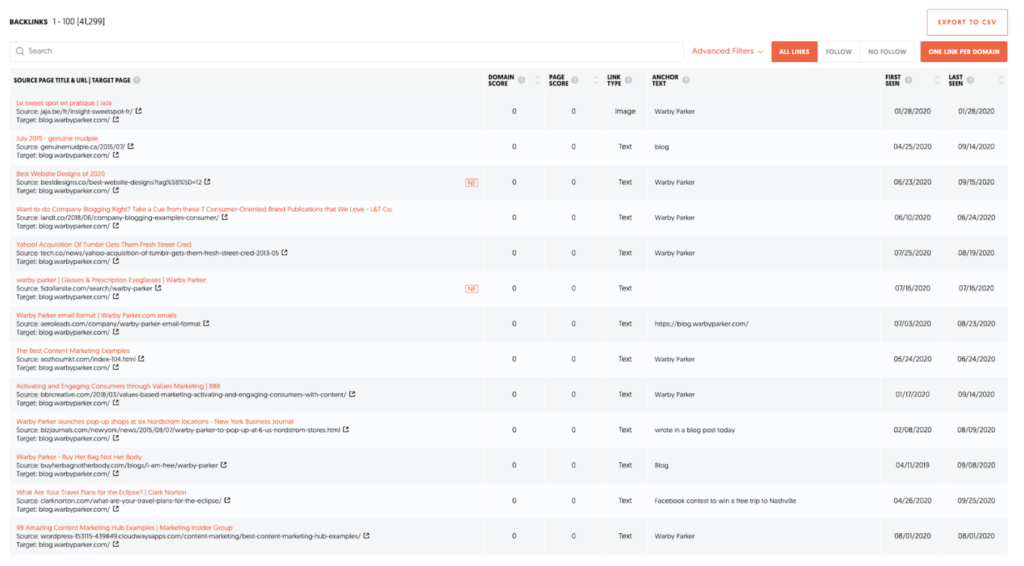
In the columns you will find:
- name and URL of the link source
- a qualitative assessment of the domain by the tool
- a qualitative assessment of the page containing the link source
- the format of the link
- the text containing the backlink, and finally
- the indexing data.
You must handle this data with care. For example, look at line 3. This is a website that lists the top website designs of 2020. I constantly wonder what these pages are good for. The website has no power to provide link juice (we called it that way a decade ago) as it is a “no follow” link. From a business point of view, it's the same because it doesn't help Warby Parker to sell a frame to a customer.
Backlinks with a high domain score, high page score, a meaningful anchor text embedded in a content that deals in detail with the Warby Parker range of products and services are the most desirable. This costs either a lot of money or a lot of persuasion.
Improving these results is the task of content marketers.
Step 7: Monitoring, reporting and analysis
Now that you have audited the website, it would be a pity if the findings were not translated into action and success measurement.
Therefore it’s important to continuously monitor all relevant metrics, such as loading times, rankings on relevant keywords, successful removal of harmful backlinks and the growth of valuable backlinks.
Some metrics are tool-specific. Therefore you should always use the same tool to measure the changes. In any case, use a second tool to validate the objective data.
Your data pool can become very large, very quickly. Therefore, only present the most relevant ones in your monthly reporting. This way you can carry out a regular target-performance comparison in this complex field.
Such reporting must of course be discussed, especially in search engine optimization, where there is a lot of room for interpretation. As mentioned at the beginning, you can only speculate how Google's artificial intelligence handles the data you can evaluate. Our assumptions only become objectifiable in field tests when we check measures over a longer period of time based on the changes.
Monitoring is best done by SEO specialists, the reporting by the content marketer, and the analysis by the whole team.
Summary
As already mentioned at the beginning, the SEO audit is a complex analysis procedure that can take several weeks to achieve a benchmark score alone. In the context of this article we have more or less only scratch the surface. These and many other topics are covered in my ebook “Website. Content. Strategy.” It contains valuable information and it’s free, so grab it now!
 Gerrit Grunert
Gerrit Grunert
Gerrit Grunert is the founder and CEO of Crispy Content®. In 2019, he published his book "Methodical Content Marketing" published by Springer Gabler, as well as the series of online courses "Making Content." In his free time, Gerrit is a passionate guitar collector, likes reading books by Stefan Zweig, and listening to music from the day before yesterday.

![[FREE Ebook] Content Marketing Tools Essentials](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/463294/02a763e7-df79-4758-ba35-000e19399736.png)







.png)










.jpg)
-1.jpg)

-1.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)













.jpg)






.jpg)





























.jpg)